Grid Credentials
Credentials are secret values that you can use to securely inject sensitive information into the Grid platform. Credentials are encrypted in the Grid-backend storage systems and are only decrypted immediately prior to use.
Access to Secrets (Teams Users)
Credentials can be created by any Grid user, with a limit of 50 Credentials per account. Only the user who created a credential (the owner) can delete that credential. All of the user's team members are able to utilize the credential in their own workflow (for example, while creating a Datastore from a private s3 bucket).
Sensitive credential type values can never be retrieved from Grid via the CLI. However,
the values of non-sensitive credential types (such as --type s3) can be viewed by the user
who created the credential and any member of the user's team (for our teams tier users.)
Credential Types
At the moment, the following credential types are supported:
s3(access for datastore creation from a private s3 bucket)
How to Create an s3 Credential for Private S3 Access (BYOC users only)
Grid now supports the ability to create Datastores from private AWS s3 buckets by using
the --no-copy mode via the CLI. In order to allow Grid to access your private buckets,
you'll need to create an authorized AWS Role using the grid credential create --type s3
command (explained in detail below). After creating a role, you can run the
grid datastore create S3://<private-bucket-name-here> --no-copy command as usual - no
modifications needed. If any of your registered s3 credentials can access the s3 bucket
path specified, then Grid will automatically use them when creating the Datastore (and
when using that Datastore in a run or session).
Prerequisite: Configure IAM Role in AWS
In order to provide Grid access to a private S3 bucket, you must first set up an AWS IAM Role configured with the appropriate permission policy. This is the absolute minimum permission Grid requires in order to list and retrieve files from an s3 bucket of your choice. The grid credential create command will dynamically generate the IAM Role Trust Policy based on the cluster on which you are creating the Datastore. While all users will need to authorize the AWS account ID on which the Grid Platform controlplane runs, bring-your-own-cloud (BYOC) users will also need to include the AWS account ID on which the BYOC cluster runs.
info
Please refer to the AWS documentation on IAM Role Trust Policies and IAM Role Permission Policies for more detailed information.
We will illustrate the process of registering an IAM Role with Grid using the following example:
I want to run an experiment or session using sensitive data contained in a private s3 bucket. The bucket's name is
gridai-demo-bucketand I would like to create a Datastore from any file prefix (folder) in the bucket.
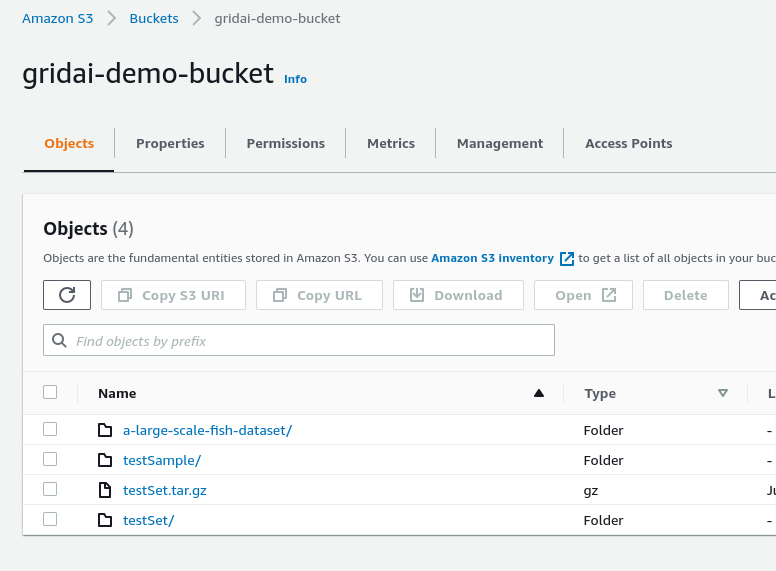
0. Change from deault cluster context
By default the cluster context is set to Grid Cloud. Change this to your BYOC cluster you created.
grid user set-cluster-context <byoc cluster name>
1. Generate Trust and Permission Policiess
First: run the grid credential create --type s3 command in order to find the required trust and
permission policies.
$ grid credential create --type s3
Please refer the the the documentation for how to create an AWS role and
permission policy.
The trust policy for the role should be:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "302180240179"
},
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"sts:ExternalId": "6aa0ae3592534df8936b03f4b73294c4"
}
}
}
]
}
The permission policy attached to the role should be:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<replace-with-bucket-name>",
"arn:aws:s3:::<replace-with-bucket-name>/*"
]
}
]
}
Please be sure to change the <replace-with-bucket-name> field with the bucket
name you wish to grant access to. More information can be found on the docs.
Please Note: when creating the role name in the AWS console, the role name MUST
begin with the prefix: grid-s3-access- any valid characters can follow the
prefix.
When complete, please enter the role ARN:
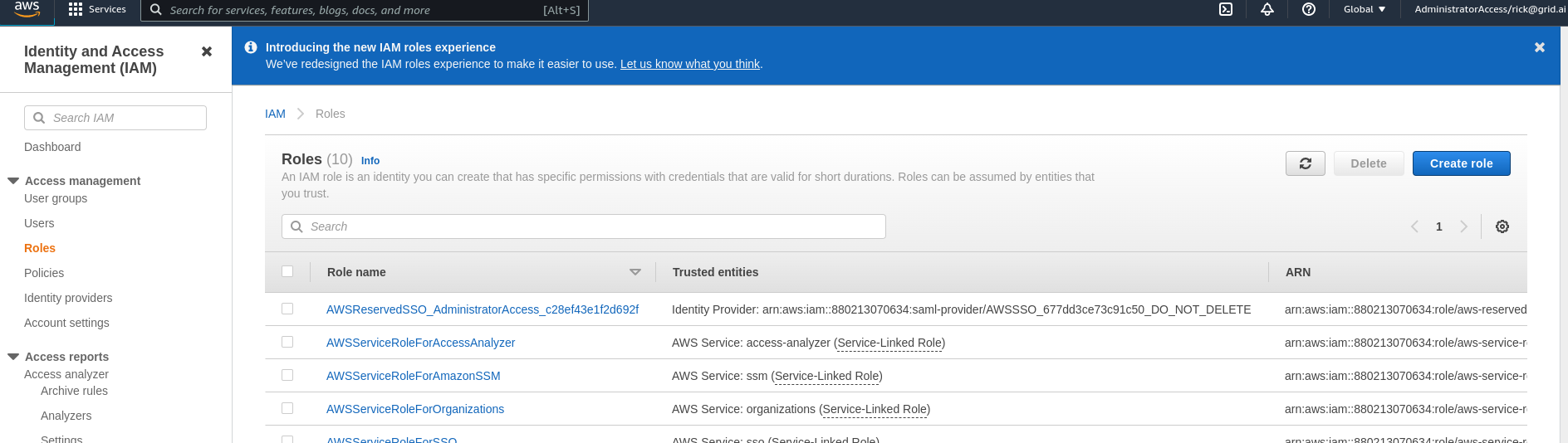
2. Add Trust and Permission Policies to AWS
The grid credential create command will output the required trust and permission policies.
a. Naviagte to AWS WebUI -> IAM -> Role
b. Create Role -> Custom trust policy
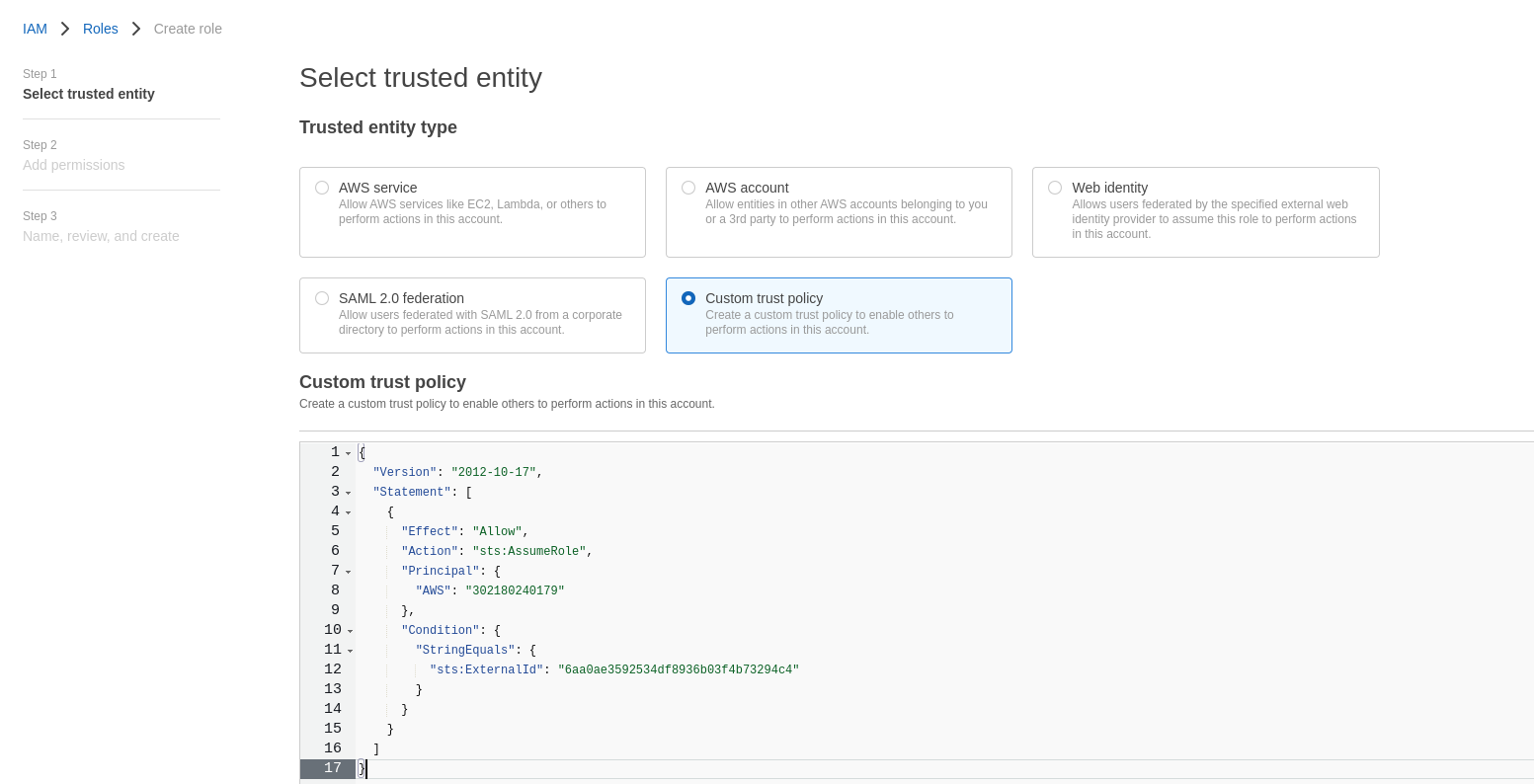
c. Paste the output of the trust policy from the CLI into the json editor and click Next
d. In the Add permissions page click Next
e. The role name must begin with grid-s3-access- and click on Create role
f. You will be redirected to IAM -> Roles. Select your just created
g. Click on Add Permissions -> Create Inline Policy. Paste the output permission policy from the CLI output after replacing your bucket name and click on Review Policy
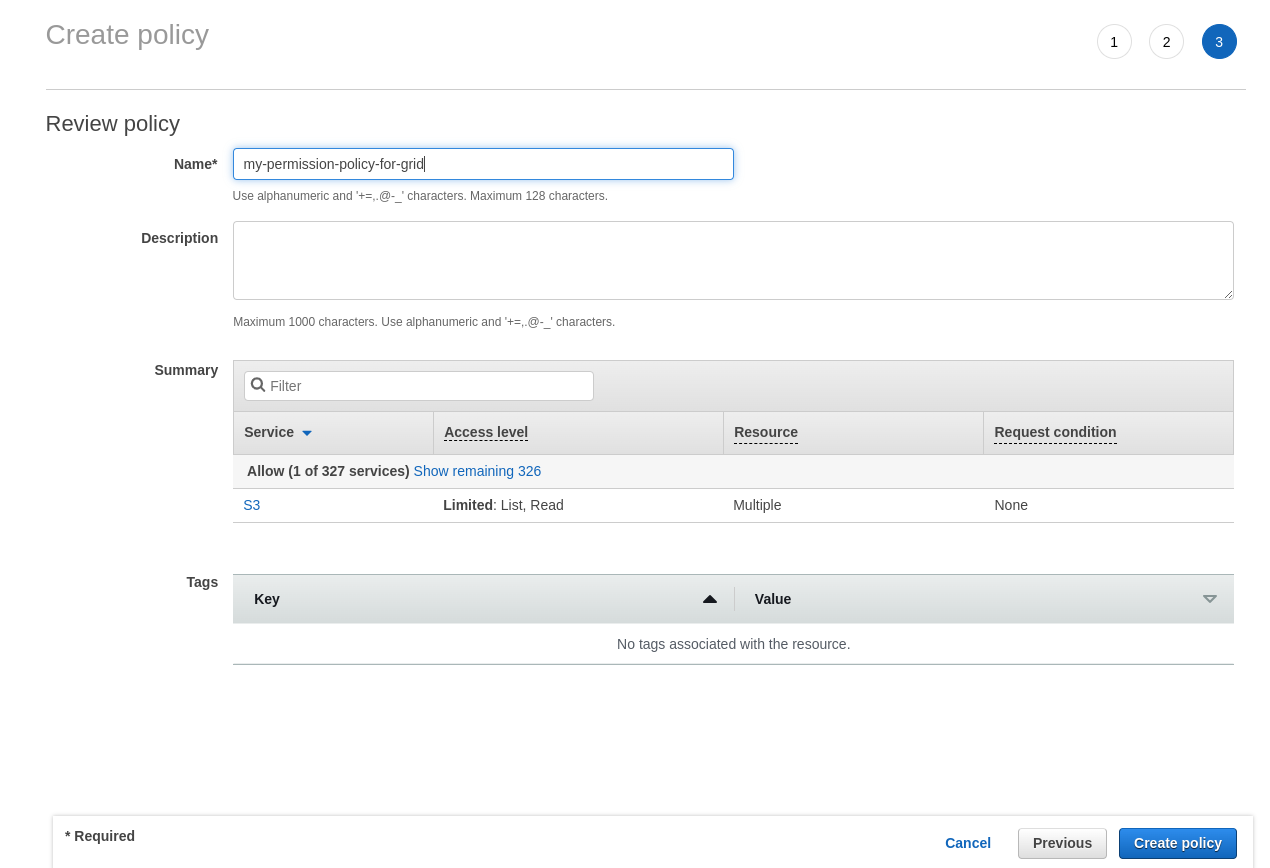
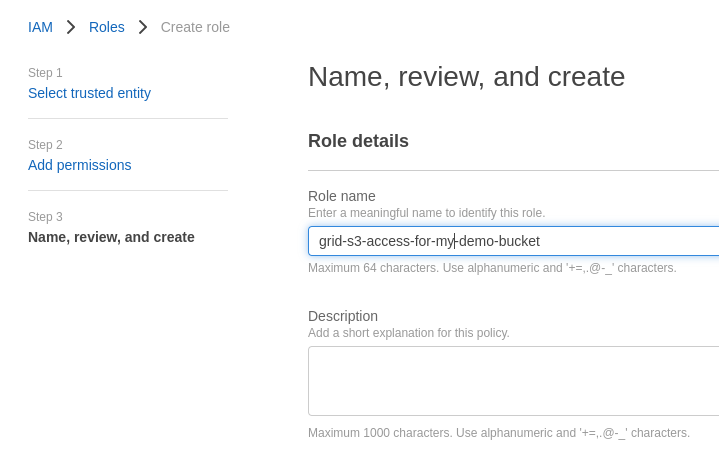
h. Enter an appropriate name, for example: my-permission-policy-for-grid
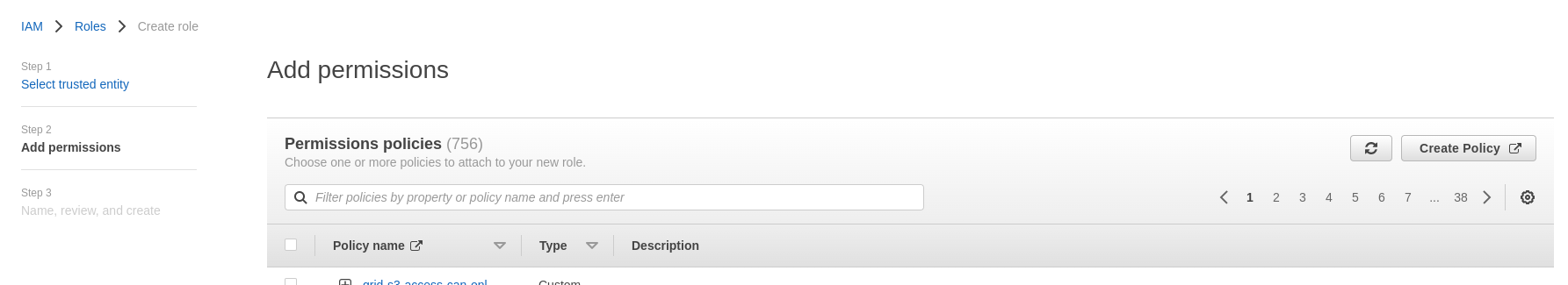
4. Input role ARN in Grid
Within Roles -> Search for the role you created that began with grid-s3-access- and click on it
Click on the icon next to the "role ARN" in order to copy the value to my clipboard:
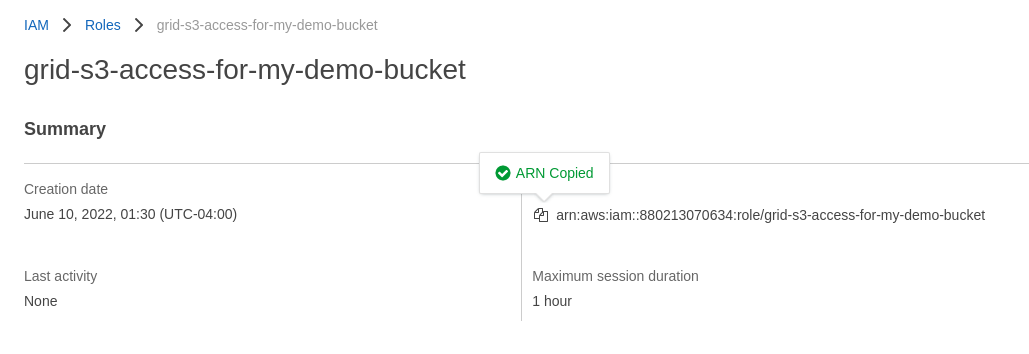
I now go back to the terminal and paste my clipboard value into the input field I am being presented with:
...
...
...
When complete, please enter the role ARN: arn:aws:iam::880213070634:role/grid-s3-access-for-my-demo-bucket
Success!
The role has been successfully added, and I can see it in the list when I run grid
credentials or grid credentials list.
I can now run the regular command to create a Datastore and it will automatically pick the correct credential and create the Datastore from my private s3 bucket!
$ grid datastore create s3://gridai-demo-bucket/ --no-copy
Success!